
All vehicles, in accordance with the current legislation, are equipped with lighting devices - headlights of various types. Read about what a car headlight is, what types of headlights are, how they work and work, as well as the correct selection, replacement and operation of headlights - read the article.
What is a car headlight?
A car headlight is an electric lighting fixture mounted at the front of a vehicle. This device provides illumination of the road and the surrounding area at low light levels, or in conditions of insufficient visibility. Headlights are often referred to as head lights or head optics, which reflects their purpose and location.
Headlights are one of the main components of automotive lighting, they solve several problems:
• Lighting of the roadway section and the surrounding area in front of the car in the dark – performs the head light;
• Road lighting in fog, snowfall, sandstorm, etc. – perform fog lights;
• Illumination of the area at a great distance outside public roads, during search and rescue operations and in other situations - perform searchlights and searchlights;
• Ensuring the visibility of the vehicle when driving on public roads during daylight hours - dipped headlights are performed in the absence or breakdown of daytime running lights.
These functions are assigned to headlights of various types and designs.
Classification of car headlights
Car headlights are divided into types according to the method of forming the light beam, purpose, applicability in various lighting schemes and device.
According to the method of forming the light beam, there are two types of headlights:
• Reflex (reflective) - traditional headlights with a reflector of parabolic or complex shape, which forms a directional beam of light;
• Projection (searchlight, lensed, headlights of a semi-ellipsoid lighting system) - modern headlights with an optical lens, which ensures the formation of a powerful light beam with a compact size of the entire device.
According to their purpose, headlights are divided into three groups:
• Basic (head light) - to illuminate the road and the surrounding area in the dark;
• Fog - to illuminate the road in conditions of insufficient visibility;
• Searchlights and searchlights - sources of directional light to illuminate the area near and at a considerable distance.
In turn, headlights are divided into three types:
• Low beam;
• High beam;
• Combined - one device can operate in low and high beam mode (but not in two modes at the same time, which is clearly spelled out in GOST).
Low and high beam headlights differ in radiation pattern and features of the luminous flux.
Dipped headlights illuminate the road directly in front of the car and prevent drivers from being dazzled in the oncoming lane. This device forms a beam inclined downwards and directed along the road, for this purpose the lamp is mounted in front of the focus of the headlight reflector, and part of the luminous flux from its filament is shielded (at the bottom). Dipped beam headlamps can form a beam with different radiation patterns:
Low and high beam headlights differ in radiation pattern and features of the luminous flux.
Dipped headlights illuminate the road directly in front of the car and prevent drivers from being dazzled in the oncoming lane. This device forms a beam inclined downwards and directed along the road, for this purpose the lamp is mounted in front of the focus of the headlight reflector, and part of the luminous flux from its filament is shielded (at the bottom). Dipped beam headlamps can form a beam with different radiation patterns:
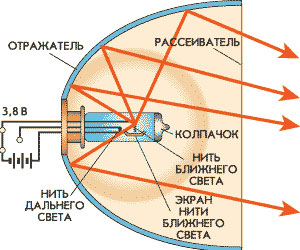
Operation of the headlamp in low beam
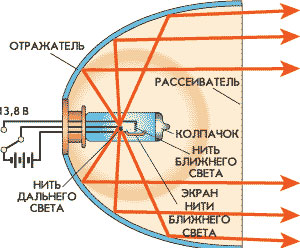
mode Operation of the headlamp in driving beam mode

• Symmetrical - the light propagates forward evenly, gradually losing intensity with a deviation from the optical axis of the headlight to the right and left;
• Asymmetric (European) - the light beam illuminates the road unevenly, the highest illumination intensity is provided on the right, covering the right lane and the shoulder, attenuation of the beam on the left prevents blinding drivers in the oncoming lane.
The high beam headlight illuminates the road and the terrain at a great distance from the car. The lamp of this headlamp is located exactly in the focus of the reflector, so a symmetrical beam of high intensity is formed, directed forward.
Headlights can be used in head optics of various schemes:
• Two-headlight scheme - two headlights of the combined type are used, located symmetrically on both sides of the middle axis of this vehicle;
• Four-headlight scheme - four headlights are used, two of which work only in low beam mode, two - only in high beam mode. The headlights are assembled in pairs of "dipped beam + high beam", the pairs are located symmetrically to the middle axis of this vehicle.
In accordance with the current legislation (GOST R 41.48-2004 (UNECE Regulations No. 48) and some others), cars must be equipped with strictly two dipped and high beam headlights, two fog lights can be optionally installed, the presence of additional dipped and high beam headlights or, conversely, the absence of standard devices is not allowed, such a car cannot be operated (according to paragraph 3 of the "Basic Provisions for the Admission of the Vehicle to Operation ..." Traffic Rules of the Russian Federation).
Design and features of car headlights
By design, headlights are divided into several types:
• Cabinet - have a separate case, can be mounted on brackets on the car body or in another place. This type includes headlights of a number of cars up to the 60s, as well as fog lights, searchlights and searchlights;
• Built-in - installed in special niches provided in the front of the car;
• Block headlights - combine dipped and high beam headlights and direction indicators into one design. Usually they are embedded;
• Headlights-lamps - lamps of increased size, Integrated into a single design with a reflector and diffuser, are built-in. The most common on American cars, today they are used much less often than conventional headlights.
Structurally, all headlights are fundamentally the same. The basis of the product is the case in which the reflector is installed - a mirror curved in a certain way (usually plastic with a metallized reflective coating), which ensures the formation of a forward-directed light beam.
There are three types of reflectors:
• Parabolic - classic design, the reflector has the shape of a paraboloid of rotation, which ensures uniform distribution of light along the optical line;
• Free-form - the reflector has a complex shape with areas that have a different inclination relative to each other, it forms a light beam with a certain radiation pattern;
• Elliptical - this is the shape of the reflectors of projection (lensed) headlights, the elliptical shape provides the necessary pattern of the light beam in a confined space.
The headlight unit uses several reflectors for all lamps integrated into a single design. A light source is installed in the center of the reflector - a lamp of one type or another (conventional, halogen, LED, xenon), in high beam headlights the filament or arc is located in the focus of the reflector, in dipped headlights it is brought slightly forward. At the front, the headlight is covered with a diffuser - a transparent part made of glass or polycarbonate, on which corrugation is applied. The presence of corrugation ensures uniform scattering of the light beam over the entire illuminated area. There is no diffuser in searchlights and searchlights, more precisely, the glass covering the lamp has no corrugation, it is smooth. In fog lamps, the lens may be painted yellow.
The design of lensed headlights is more complex. They are based on an elliptical reflector, in the focus of which a lamp is installed, and at some distance - an optical collecting lens. Between the lens and the reflector there may be a movable screen that changes the light beam when switching between low beam and high beam.
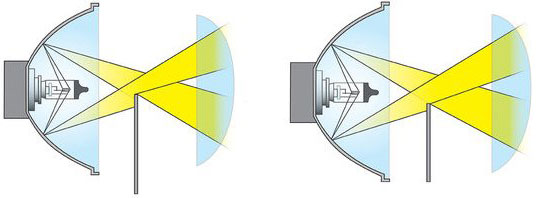
The overall design and operation of the lensed car lamp
The body and lens of the headlamp are marked with its main characteristics and the types of lamps that can be installed. Installation of other light sources is unacceptable (with rare exceptions), this can change the characteristics of the headlight, and as a result, the vehicle will not pass inspection.
Issues of selection, replacement and operation of car headlights
To choose new optics, it is necessary to take into account the design, features and characteristics of old products, ideally you should buy a headlight of the same model. If we are talking about fog lights or searchlights and searchlights that were not on the car, then here you should take into account the possibility of installing these devices on the car (the presence of appropriate brackets, etc.) and their characteristics.
Special attention should be paid to the choice of headlights. Today, they are usually presented in two versions - with a transparent (white) and yellow segment of the turn signal. When choosing a headlight with a yellow turn signal segment, you need to buy a lamp with a transparent bulb, when choosing a headlight with a white turn signal segment, you need to buy a lamp with a yellow (amber) bulb.
Replacement of headlights is carried out according to the instructions for operation and repair of the car. After replacement, it is necessary to adjust the headlights according to the same instructions. In the simplest case, this work is performed using a screen - a vertical plane with markings on which the headlights are directed, a wall, garage door, fence, etc. can act as a screen.
For European-style low beam (with asymmetric beam), it is necessary to ensure that the upper limit of the horizontal part of the light spot is located just below the center of the headlights. To determine this distance, you can use the following formula:
h = H–(14×L×H)/1000000
where h is the distance from the axis of the headlights to the upper boundary of the spot, H is the distance from the road surface to the center of the headlights, L is the distance from the car to the screen, the unit of measurement is mm.
For adjustment, it is necessary to put the car at a distance of 5-8 meters from the screen, the value h should lie in the range of 35-100 mm, depending on the height of the car and the location of its headlights.
For the high beam, it is necessary to ensure that the center of the light spots lies about half the distance from the optical axis of the headlamp and the border of the low beam light spot. Also, the optical axes of the headlights should be directed strictly forward, without deviations to the sides.
With the right choice and adjustment of headlights, the car will receive high-quality lighting equipment that meets the requirements of standards and ensures safety on the road when driving in the dark.
Post time: Aug-22-2023
