
In every modern car, tractor and other vehicles, several dozen lighting devices are used - lamps. Read about what a car lamp is, what types of lamps there are and how they are arranged, how to choose and operate lamps of various types - read in this article.
What is a car lamp?
A car lamp is a lighting electrical device, an artificial light source in which electrical energy is converted into light radiation in one way or another.
Car lamps are used to solve several problems:
• Illumination of the road and the surrounding area in the dark or in conditions of insufficient visibility (fog, rain, dust storm) - headlights, fog lights, searchlights and searchlights;
• Road safety warning lights – direction indicators, brake lights, reversing signal, daytime running lights, rear license plate illumination, rear fog lights;
• Alarm about the condition of the car, its components and assemblies - signal and control lamps on the dashboard;
• Interior lighting – car interior, engine compartment, luggage compartment;
• Emergency lighting – remote carrying lamps and others;
• Tuning and modernization of cars - decorative lighting lamps.
To solve each of these problems, lamps and other light sources (LEDs) of different design and characteristics are used. To make the right choice of lamp, you first need to understand their existing types and features.
Types and characteristics of automotive lamps
Automotive lamps can be divided into types and types according to the underlying physical principle, characteristics and purpose.
According to the physical principle of operation, lamps are divided into the following types:
• Incandescent lamps;
• Xenon gas-discharge (arc, xenon-metal halide);
• Gas-light lamps (neon and filled with other inert gases);
• Fluorescent lamps;
• Semiconductor light sources – LEDs.
Each of the described types of lamps has its own design features and principle of operation.
Incandescent lamps. The light source is a tungsten filament heated to a high temperature, enclosed in a glass flask. They can have one or two filaments (combined low and high beam lamps), there are three types:
• Vacuum - air is pumped out of the flask, due to which the filament does not oxidize when heated;
• Filled with an inert gas - nitrogen, argon or a mixture of them is pumped into the flask;
• Halogen - the bulb contains a mixture of halogen vapors of iodine and bromine, which improves the operation of the lamp and its characteristics.
Vacuum lamps today are used only in instrument panels, in illumination, etc. Universal lamps filled with inert gases are widespread. Halogen lamps are used only in headlights.
Xenon lamps. These are electric arc lamps, there are two electrodes in the bulb, between which an electric arc burns. The bulb is filled with xenon gas, which provides the necessary characteristics of the lamp. There are xenon and bi-xenon lamps, they are similar to lamps with two filaments for low and high beam.
Gas-light lamps. These lamps use the ability of inert gases (helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon) to emit light when an electric discharge passes through them. The most widely used neon lamps are orange, argon lamps give a purple glow, krypton lamps give a blue glow.
Fluorescent lamps. In these lamps, light emits a special coating inside the bulb - a phosphor. This coating glows due to the absorption of energy, which in the form of ultraviolet light is emitted by mercury vapor when an electric discharge is passed through them.
LED lamps. These are semiconductor devices (light-emitting diodes) in which optical radiation arises as a result of quantum effects in the p-n junction (at the point of contact of semiconductors of different properties). LED, unlike most other light sources, is practically a point source of radiation.
Lamps of various types have certain applications:
• Incandescent lamps are the most versatile, today they are used for head lights, alarms, in the cabin, as control and signal lamps in dashboards, etc.;
• Xenon - only in the head light;
• Gas-light - neon lamps as indicator and control lamps (rarely used today), neon and other gas tubes for decorative lighting;
• Fluorescent - as salon (rarely) and remote light sources for emergencies, repairs, etc.;
• LEDs are universal light sources that are used today in head lights, for light signaling, as daytime running lights, in instrument panels.

LED lamp type H4
Car lamps have several main characteristics:
• Supply voltage – 6, 12 and 24 V, respectively for motorcycles, cars and trucks;
• Electrical power - the power consumed by the lamp usually ranges from tenths of a watt (signal and control lamps) to several tens of watts (headlight lamps). Usually, parking lamps, brake lights and direction indicators have a power of 4-5 watts, head lamps - from 35 to 70 watts, depending on the type (incandescent lamps - 45-50 watts, halogen lamps - 60-65 watts, xenon lamps - up to 75 watts or more);
• Brightness - the power of the luminous flux created by the lamp is measured in lumens (Lm). Conventional incandescent lamps create a luminous flux of up to 550-600 Lm, halogen lamps of the same power - 1300-2100 Lm, xenon lamps - up to 3200 Lm, LED lamps - 20-500 Lm;
• Color temperature is a characteristic of the color of the lamp radiation, indicated in degrees Kelvin. Incandescent lamps have a color temperature of 2200-2800 K, halogen lamps - 3000-3200 K, xenon lamps - 4000-5000 K, LED lamps - 4000-6000 K. The higher the color temperature, the lighter the lamp is.
Separately, there are two groups of lamps according to the radiation spectrum:
• Conventional lamps - have a bulb of ordinary glass, emit in a wide spectrum (in the optical and near-ultraviolet and infrared regions);
• With an ultraviolet filter - have a flask made of quartz glass, which retains ultraviolet radiation. These lamps are used in headlights with a diffuser made of polycarbonate or other plastics, which lose their qualities and are destroyed by UV radiation.
However, the above characteristics when choosing lamps are not as important as their design and type of base, which needs to be said in more detail.
Types of caps, design and applicability of automotive lamps
Today, lamps with a wide variety of bases are used, but they are all divided into two large groups:
• Europe - lamps manufactured in accordance with UNECE Regulation No. 37, this standard is also adopted in Russia (GOST R 41.37-99);
• America - lamps manufactured in accordance with NHTSA (National Highway Traffic Safety Administration) regulations, some types of lamps have European counterparts.
Regardless of the group, lamps can have bases of the following types:
• Flanged - the base has a restrictive flange, the electrical connection is made by flat contacts;
• Pin - the base is made in the form of a metal cup with two or three pins for fixing in the cartridge;
• With a plastic socket (rectangular base) - flanged lamps with a plastic socket with an integrated connector. The connector can be located on the side or at the bottom (coaxial);
• With a glass base - the base is part of a glass bulb, electrical contacts are soldered in its lower part;
• With a glass cap and a plastic chuck - a plastic chuck with or without a connector is located on the side of the cap (in this case, the contacts from the cap pass through the holes in the chuck);
• Soffit (two-based) - cylindrical lamps with bases located at the ends, each terminal of the spiral has its own base.
At the same time, lamps with different types of bases are divided into groups according to their purpose:
• Group 1 - without restrictions - low and high beam lamps, fog lamps, etc. This group includes all lamps of types (categories) H (the most common is type H4), HB, HI, HS, as well as some special lamps (S2 and S3 for motorcycles and mopeds, and others);
• Group 2 - warning lamps, turn signal lamps, reversing lamps, parking lights, license plate illuminations, etc. This group includes lamps marked C, HY, P, PR, PY, PR, PSR, PSY, R, T, W and some others;
• Group 3 - lamps for the replacement of similar products in discontinued vehicles. This group includes lamps R2 (with a round bulb, widely used on old domestic cars), S1 and C21W;
• Xenon discharge lamps - this group includes xenon lamps marked D.
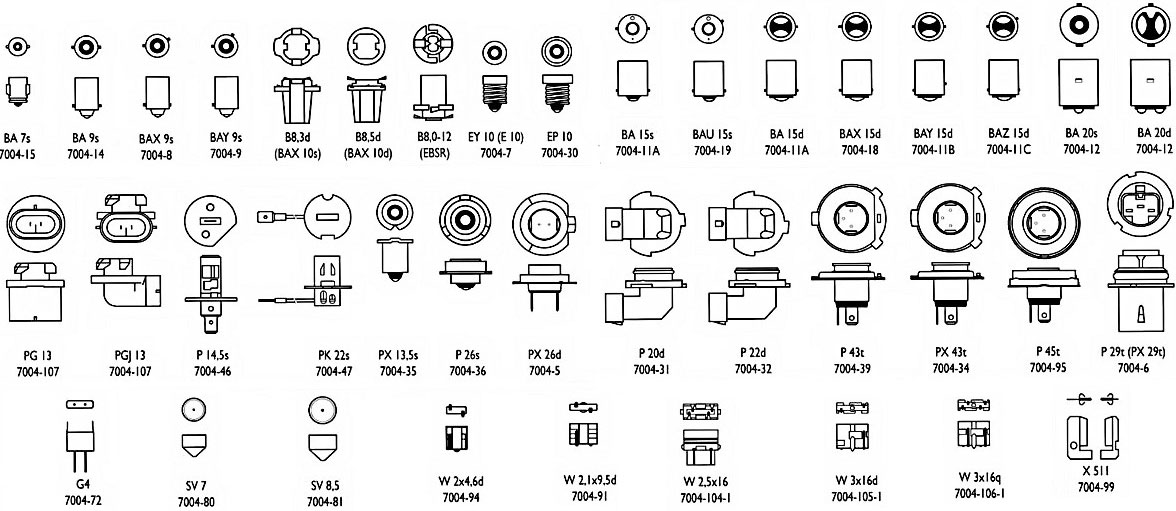
Types of car lamp
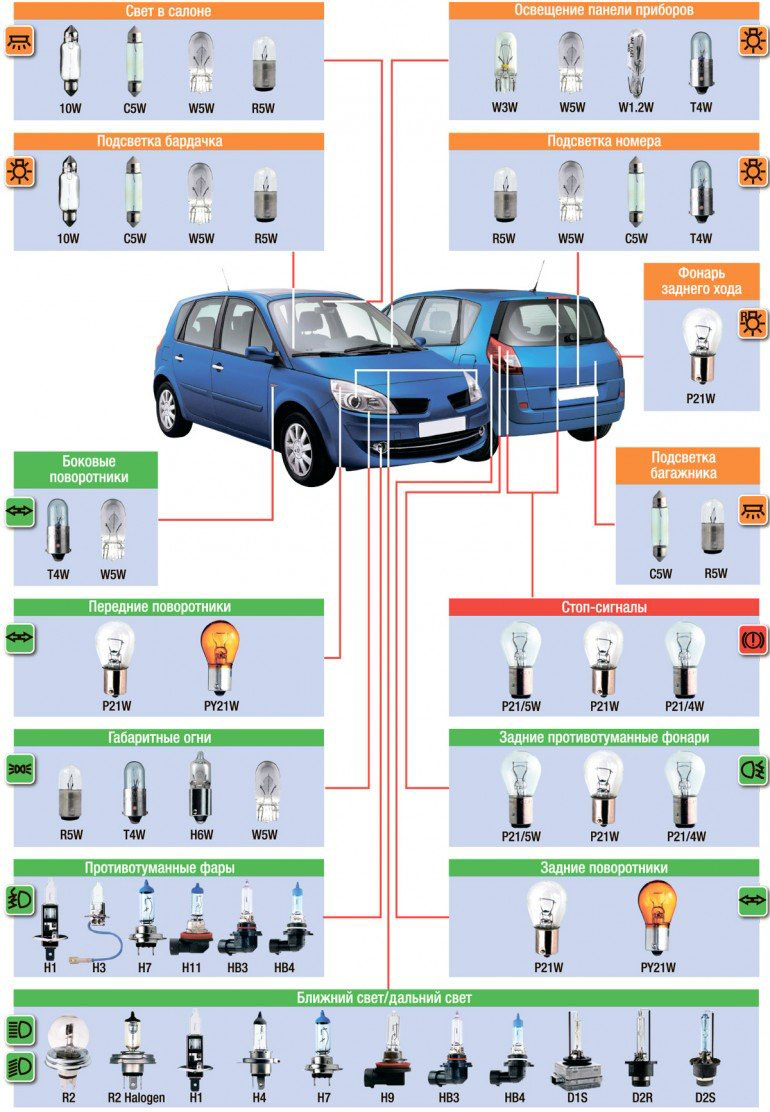
caps Applicability of the main types of car lamps
There are two types of Group 1 lamps used for headlights:
• With one filament (or one arc in the case of a xenon lamp) - used only as a dipped or high beam lamp. In passing beam devices, the filament at the bottom is covered by a specially shaped screen so that the light flux is directed only to the upper part of the headlamp reflector;
• With two filaments - used as a dipped and high beam lamp. In these lamps, the filaments are separated by a certain distance so that when installed in the headlight, the high beam filament is in the focus of the reflector, and the dipped beam filament is out of focus, and the dipped beam filament is closed from the bottom of the screen.
It should be especially noted that the type (category) of the lamp and the type of base are not the same thing. Different groups of lamps differ in design and may have a standardized base, the most common types of bases are shown in the figure.
The correct choice and features of operation of car lamps
When choosing lamps in a car, you should take into account the type of lamp, the type of its base and electrical characteristics - supply voltage and power. It is best to buy lamps with the same markings that the old ones had - this way you are guaranteed to get exactly what you need. If, for one reason or another, it is not possible or desirable to purchase exactly the same lamp (for example, when replacing conventional incandescent lamps with LED ones), then the type of base and electrical characteristics should be taken into account.
When choosing lamps for the head light, you need to take into account the recommendations of the car manufacturer indicated on the diffuser. So, for plastic diffusers (and there are most of them today), you need to buy lamps with an ultraviolet filter - almost all halogen lamps are produced as such. Also, on the diffuser, the marking of suitable lamps can be indicated or their type can be indicated (for example, the inscription "Halogen"). It is best to buy lamps in pairs so that both headlights have identical characteristics.
When buying lamps for direction indicators and repeaters, you need to take into account the color of their diffusers. If the diffuser is transparent, then it is necessary to choose lamps with a bulb of the so-called automobile yellow (amber) color. If the diffuser is painted, then the lamp should have a transparent bulb. It is impossible to replace one type of lamp with another (for example, put an amber lamp instead of a transparent one or vice versa), since they have different types of bases and are not interchangeable.
Care must be taken when installing lamps, especially head lights. You can take the lamp only by the base or use clean gloves. The remnants of grease from the fingers and dirt on the bulb lead to negative consequences - the radiation pattern of the lamp and the characteristics are violated, and due to uneven heating, the lamp can crack and fail after a few hours of operation.
With proper selection and replacement of lamps, the car will meet the requirements of standards and provide comfortable operation in various conditions.
Post time: Aug-21-2023
